In this post, we’ll demonstrate the process of adding a new filegroup to a database in SQL Server. While many databases function efficiently with a single data/log file, there are scenarios where adding a filegroup proves beneficial.
Filegroups, as outlined in the demo below, serve as a way to group user-defined data files. The example involves creating a new filegroup with two additional data files.
What are Filegroups in SQL Server?
SQL Server typically operates with two types of files: data files (.mdf) and log files (.ldf). Introducing additional data files, known as user-defined (.ndf) data files, is a common practice. Filegroups in SQL Server, on the other hand, are a means of grouping these user-defined data files.
Best Practices for Working with Filegroups
Database Administrators often add new data files to enhance database performance, especially when dealing with multiple databases on an instance. This practice involves splitting data files and distributing data across multiple disk drives. Another instance where adding a new data file is advisable is when configuring Change Data Capture (CDC). For CDC, creating a separate filegroup is considered a best practice.
For more recommendations for working with Filegroups in SQL Server, check out the Mircosoft Documentation: Database Files and Filegroups: Recommendations
Adding a New Filegroup for a Database
The following SQL script illustrates the creation of a Filegroup and the addition of two new data files:
-- Create a test database CREATE DATABASE [sqlDBA]; USE [sqlDBA]; GO -- Create test tables & insert rows from system tables SELECT * INTO dbo.raw_sysdatabases FROM sys.databases; SELECT * INTO dbo.raw_sysobjects FROM sys.system_objects; -- Create a filegroup ALTER DATABASE [sqlDBA] ADD FILEGROUP [sqlDBA_FG1]; -- Check filegroups for the current database SELECT * FROM sys.filegroups;
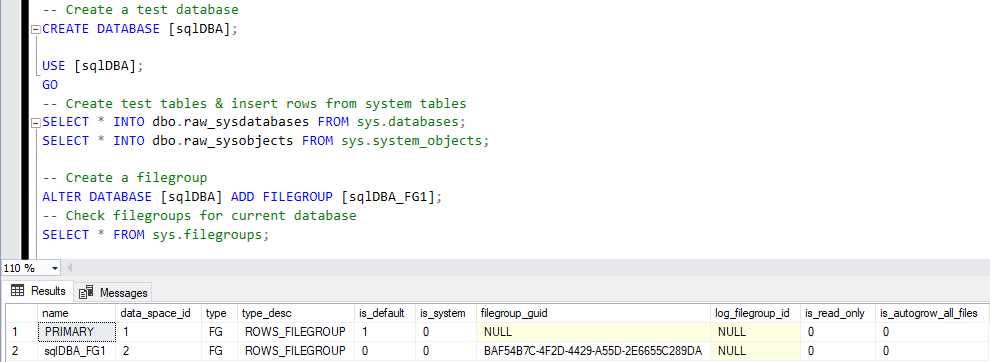
We’re using ALTER DATABASE to add a Filegroup to the sqlDBA database. Then, we add the new data files to the Filegroup in the database:
-- Create data files for Filegroup
ALTER DATABASE [sqlDBA]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = sqldba_data1,
FILENAME = 'D:\mssql_data\sqldba_data1.ndf',
SIZE = 500MB,
FILEGROWTH = 50MB
),
(
NAME = sqldba_data2,
FILENAME = 'D:\mssql_data\sqldba_data2.ndf',
SIZE = 500MB,
FILEGROWTH = 50MB
) TO FILEGROUP [SQLDBA_FG1];
-- Check files for a database
USE [sqlDBA];
GO
SELECT
file_id, type, type_desc, data_space_id, name,
physical_name, state, size, max_size, is_percent_growth, growth
FROM sys.database_files;
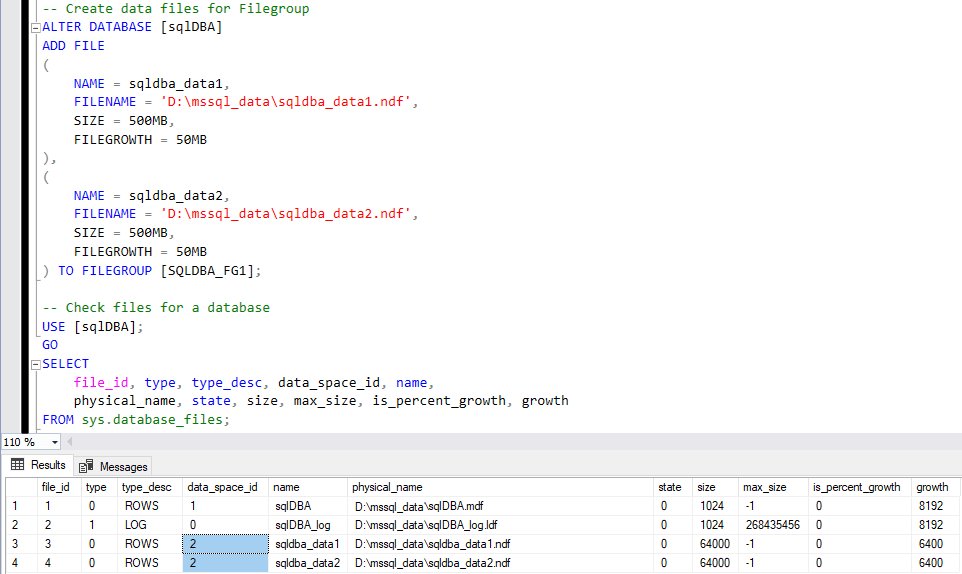
In the example above we have successfully added 2 new database files to the sqldba database.
For more information on the ALTER DATABASE SQL Command being used, feel free to refer to the MS Docs Examples:
– Adding a file to a database
– Adding a filegroup with two files to a database
Inspect New Filegroup and Data Files
To view our new database files via GUI, navigate to the “Shrink Databases” option in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
SSMS > Right-Click Database > Tasks > Shrink:
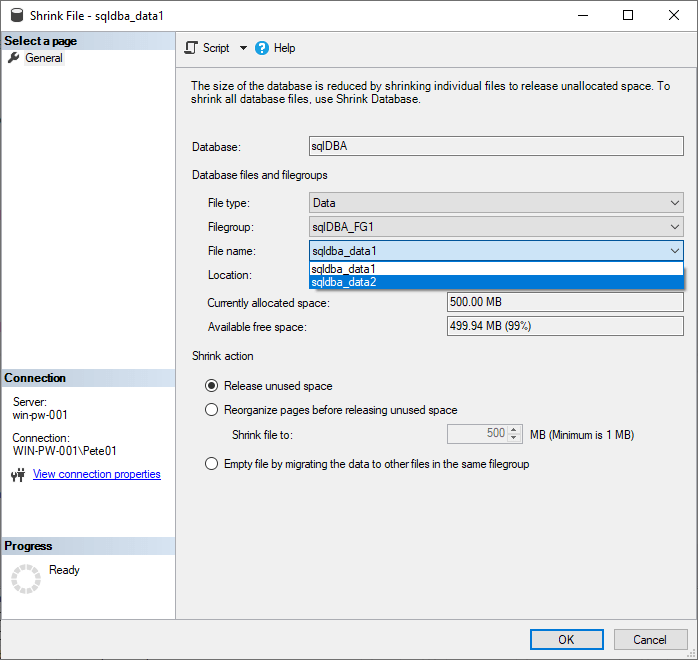
By following this step-by-step guide, you’ve successfully added a filegroup to a database in SQL Server, enhancing your database management capabilities.
Stay tuned for more insightful tips and tutorials!
