Discovering the processes associated with TCP or UDP ports on a Windows host is crucial for various reasons, from validating service ports to proactively addressing potential security concerns. This guide will show two efficient methods to quickly identify and analyze listening ports on a Windows system.
Whether you opt for the already available Windows Resource Monitor or download the TCPView application for a more detailed view, these methods should hopefully provide you with what you need for in-and-out information about a system’s network activity.
How to Check Listening Ports in Windows
Method 1: Resource Monitor
Utilizing Resource Monitor provides an accessible GUI option to inspect detailed listings of TCP and UDP endpoints on your machine. Follow these steps:
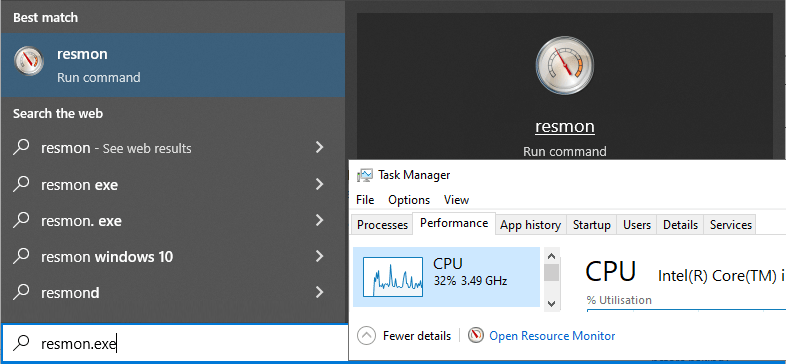
1. Open Resource Monitor:
Navigate to resmon.exe or access it through Task Manager’s Performance tab.
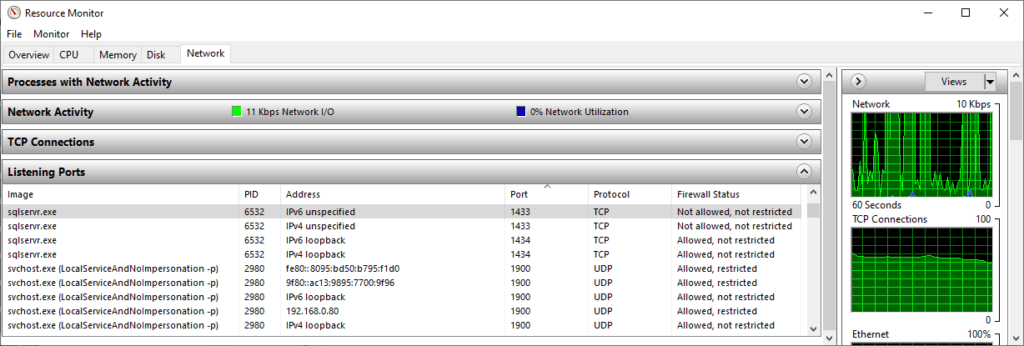
2. Explore Listening Ports:
Within Resource Monitor, go to the Network tab and expand the “Listening Ports” section.
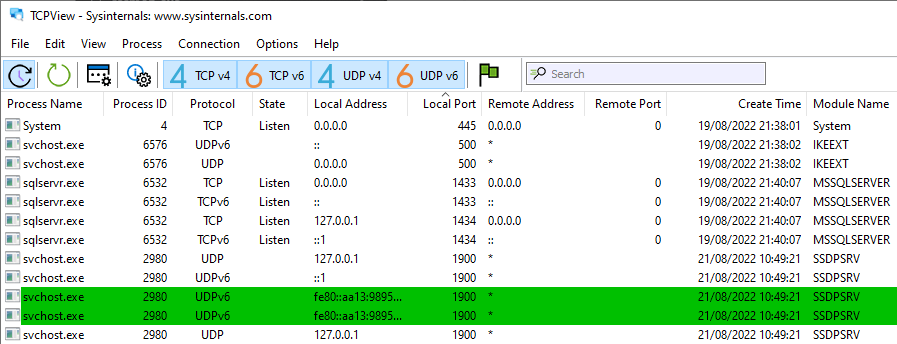
Method 2: TCPView (Sysinternals Tool)
TCPView offers a rapid and lightweight solution for visualizing all TCP and UDP endpoints on your system. Ideal for users seeking efficient filtering and search functionality, TCPView ensures a quick and comprehensive view of the information you need.
1. Download TCPView:
Obtain TCPView from Sysinternals within seconds.
2. Launch TCPView:
Open the application to reveal a detailed overview of TCP and UDP endpoints.
Additional Tips
1. Understanding Port Status:
Monitor the status of listening ports to quickly identify active or waiting connections, aiding in the prompt detection of potential issues or security risks. Additionally, pay attention to the firewall status in the Resource Monitor’s Listening Ports view – if not allowed, consider adding the necessary rule to ensure seamless connectivity.
2. Filtering Options in TCPView:
Utilize TCPView’s advanced filtering options to narrow down your search based on specific criteria such as protocol, process, or port number, enhancing the identification process in environments with numerous active connections.
3. Monitoring Real-Time Changes:
Keep an eye on real-time changes in Resource Monitor or TCPView to detect sudden spikes in network activity or unexpected alterations, signaling potential irregularities.